Understanding Piraminds: A Historical Overview
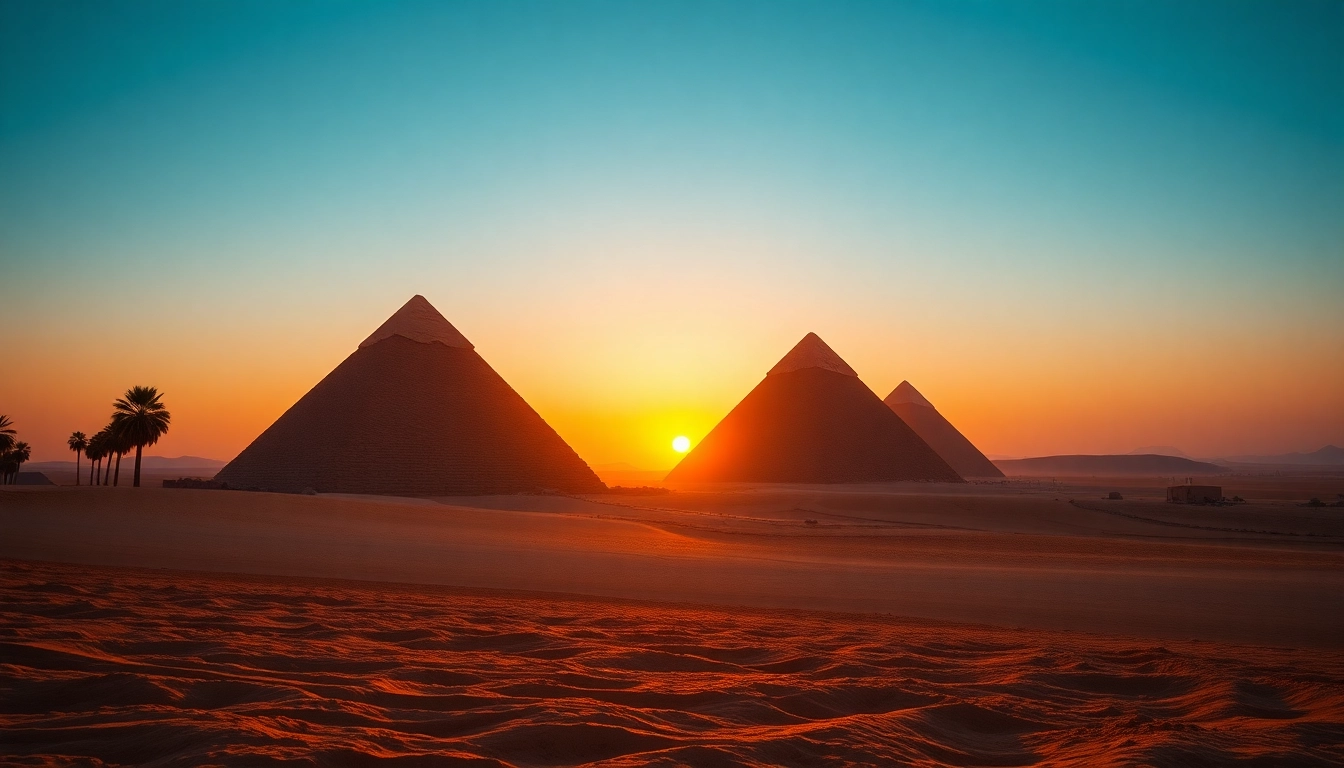
Piraminds have captivated the imagination of people across the globe for centuries, representing not just architectural wonders but also the spiritual and cultural essence of ancient civilizations. These monumental structures, synonymous with the great pyramids of Egypt, continue to inspire fascination and inquiry. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the origins, purposes, architectures, and the enduring legacy of piraminds. For a deeper understanding of these structures, you can explore piraminds and their historical significance.
1. Origins of Piraminds in Egypt
The history of piraminds can be traced back to ancient Egypt during the Old Kingdom around 2700 BCE. Initially, tombs for the elite were constructed in a simple rectangular format known as mastabas. Over time, the designs became more elaborate, leading to the creation of the iconic step pyramid, and eventually, the true pyramids we recognize today.
The most famous of these, the Great Pyramid of Giza, was built for Pharaoh Khufu and is estimated to have been constructed over a 20-year period. The evolution of the design reflects the Egyptians’ cosmological beliefs, as the pyramids were meant to facilitate the pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife, symbolizing a ladder to the heavens.
2. Purpose and Cultural Significance
The primary purpose of piraminds was to serve as tombs for pharaohs and high-ranking officials. These structures were not only burial sites but also centers of worship and were often part of a larger funerary complex that included temples and various smaller tombs. The ancient Egyptians believed in an afterlife where the deceased would need their earthly possessions, which resulted in elaborate burial practices.
Moreover, piraminds stood as symbols of power and prestige, showcasing the advanced architectural and engineering skills of the ancient Egyptians. The construction of these structures also served societal purposes, fostering an identity and unity among the ancient Egyptians around their shared cultural and religious beliefs.
3. Architectural Innovations of Piraminds
The architecture of piraminds represents a blend of creativity, engineering, and a deep understanding of geometry. The transition from the step pyramid to the smooth-sided pyramid required innovative techniques in design and construction. Engineers utilized local limestone, granite, and basalt to construct these colossal edifices. The precision in the alignment of the pyramids with the cardinal points reveals the Egyptians’ sophisticated astronomical knowledge.
Integrating ramps, levers, and various lifting mechanisms, the builders demonstrated a remarkable grasp of physics and material endurance. Moreover, the interior chambers’ design, with their intricate passage systems, showcased not only functionality but also an artistic expression pertinent to the afterlife beliefs of ancient Egyptians.
The Construction Techniques of Piraminds
1. Tools and Materials Used
The construction of piraminds relied on a range of tools and materials, primarily sourced locally. Workers utilized hand tools made from copper, stones, and wood to carve and transport the massive blocks of stone. Each stone block could weigh between 2.5 to 15 tons, requiring innovative techniques for transport and assembly.
For setting these stones in place, simple machines such as levers and sledges, often lubricated with water or oil to reduce friction, were essential. Additionally, the construction sites would have been organized, with a considerable labor force and skilled artisans executing their tasks with precision and coordination.
2. Labor Force Behind the Construction
Though popular belief suggests that slaves built the pyramids, recent evidence indicates that a large, skilled workforce of laborers undertook these constructions as a form of civic duty. Workers were organized into teams, often referred to as “gangs,” where they were provided food, shelter, and medical care. This workforce comprised skilled masons and laborers, reflecting a complex socio-economic structure underpinning pyramid construction.
The collaborative effort also fostered a sense of community among laborers, who took pride in their role in creating enduring monuments that symbolized both religious faith and national pride.
3. Engineering Marvels of the Piraminds
The engineering of piraminds is considered a marvel of ancient architecture. The Great Pyramid of Giza stands as the most impressive, displaying a base that covers over 13 acres and a height that originally reached 146.6 meters. Its precision in design and execution, including the perfect alignment with true north, showcases the high degree of knowledge attained in surveying and mathematics by the ancient Egyptians.
Additionally, the internal structure of the pyramids often included complex passageways and multiple chambers, designed to prevent tomb robbers from easily accessing the burial sites. The clever engineering of these piraminds contributes to their longevity, preserving them for thousands of years.
Exploring the Mysteries of Piraminds
1. Hidden Chambers and Passageways
Recent advancements in technology, including radar and thermal imaging, have led to the discovery of previously unknown chambers and passageways within some pyramids. For instance, the ScanPyramids project has revealed anomalies within the Great Pyramid, indicating that concealed spaces may exist. These findings excite the archaeological community, as they could provide further insights into burial practices and the religious significance attached to these structures.
The ongoing exploration of these hidden features may alter our understanding of how piraminds were constructed and the purposes they served. The new findings prompt further archaeological investigations and could unlock more secrets of ancient Egyptian civilization.
2. Theories of Construction
Despite extensive research, many aspects of pyramid construction remain shrouded in mystery. Various theories attempt to explain how these gigantic structures were built, including ramp theories, counterweight systems, and even the possibility of internal spiral ramps. Each theory presents logical arguments, but definitive proof remains elusive.
Discussions often involve innovative approaches, suggesting that ancient Egyptians may have used a combination of various techniques adapted throughout the years to suit the specific challenges posed by each pyramid’s unique structure. This encourages ongoing research and debate within the archaeological and engineering communities.
3. Archaeological Discoveries Related to Piraminds
Numerous archaeological discoveries related to piraminds have enriched our understanding of ancient Egypt. Excavations at sites like Giza have unearthed tools, worker camps, and ancillary structures that provide context to the grand construction efforts. Such finds help historians and archaeologists piece together the daily lives of those who built the pyramids.
Additionally, the discovery of inscriptions and artifacts within the burial networks offers vital clues about the rituals and beliefs surrounding death and the afterlife, shedding light on the cultural significance of piraminds within ancient Egyptian society.
Modern Implications of Piraminds
1. Impact on Tourism and Economy
Piraminds have become one of the leading attractions in Egypt, drawing millions of tourists each year. Their economic impact cannot be understated, as tourism significantly contributes to national revenue and local employment. Hotels, restaurants, and various services thrive in areas surrounding these historic sites, showcasing their broad influence on the economy.
Efforts to promote sustainable tourism practices continue to grow, aimed at preserving these treasures for future generations while maximizing their economic benefits. Additionally, educational programs and guided tours help disseminate knowledge about these architectural wonders.
2. Preservation Efforts and Challenges
The preservation of piraminds poses ongoing challenges due to natural erosion, environmental factors, and human impact. Initiatives to conserve the pyramids include collaborations between government, archaeological organizations, and international experts. Projects focus on stabilizing structures, controlling visitor access, and restoring surrounding landscapes to mitigate damage.
Promoting awareness of the necessity for conservation can enhance public support, encouraging responsible visitation while safeguarding these historically significant monuments.
3. Piraminds in Popular Culture
Piraminds permeate popular culture, appearing in films, literature, and art, reflecting their enduring allure and connection to mystery. Movies exploring themes of ancient Egypt often utilize pyramids as backdrops, reinforcing their iconic status. Video games and novels featuring these structures further illustrate their universal appeal as symbols of adventure and discovery.
The presence of piraminds in modern media serves to educate audiences worldwide about their history, inviting fascination and encouraging further exploration of ancient civilizations.
FAQs: Common Questions About Piraminds
1. What were the primary purposes of piraminds?
Piraminds primarily served as tombs for pharaohs and high-status individuals. They symbolized strength and facilitated the journey to the afterlife.
2. How were piraminds built?
Piraminds were built using large limestone and granite stones. Workers employed ramps, sledges, and other techniques to transport and position the stones.
3. What materials were used in their construction?
Main materials included limestone, granite, and basalt, often quarried locally and used in massive blocks for the structure.
4. Are there any unknown chambers within piraminds?
Recent technologies have revealed potential hidden chambers in some pyramids, indicating undiscovered areas that could hold more secrets.
5. How do piraminds affect modern tourism?
Piraminds significantly boost tourism and the economy in Egypt, attracting millions of visitors and driving local businesses while fostering interest in ancient history.